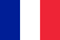
Insulin - the hormonal secret of the processor, plays an important role, ensuring the constancy of blood glucose. Diabetes mellitus is a consequence of a deficiency of this hormone. The complications caused by the disease often lead to death. The basic principles of treatment of diabetes are strict adherence to diet, taking drugs or insulin injections, tracking the glucose level of blood, observing your body so as not to miss the first signs of complications.

Pathogenesis of the disease
Diabetes mellitus is a persistent violation of the synthesis of insulin hormone and its interaction with tissues in the body.
Insulin processes the received sugar into glucose and passes it through cell membranes. Thus, the hormone lowers the degree of blood sugar and supplies the cells with nutrition. Insulin deficiency with impaired tissue sensitivity leads to the fact that glucose does not participate in metabolism and continues to circulate through the body. The biology of not only carbohydrate metabolism is lost, but also fat, protein, water-salt.
The rise of sugar increases the amount of lipid fractions in the bloodstream, which contributes to the development of atherosclerosis. The transformation of glucose into glycogen slows down, and the body begins to use fat as resources. Fatty acids break down and ketone bodies appear that cause damage to the central nervous system.
Causes and current
Insulin production is disturbed due to damage to synthesizing beta cells. The main risk factor for diabetes is heredity, which significantly enhances the effect of other factors. The probability of getting sick increases with age. The causes of diabetes:
- The failure of the immune system. Provokes the attack of cells with a pancreas with protective proteins.
- Obesity. Reduces the reaction of the receptors to the hormone due to an excess of adipose tissue (the cause of the type of type of diabetes).
- Pancreatic disease. Call the death of cells secreting the hormone (pancreatitis, cancer).
- Infection of viruses (pathogens of chickenpox, rubella, influenza).
- Nervous tension.
The disease exists in the role of independent pathology and as a temporary symptom. The causes of diabetes mellitus may be the consequences of the errors of the work of endocrine organs (hyperthyroidism, pheochromocytoma). The symptomatic excess of glucose detected during pregnancy (including using IVF) is called gestational diabetes. Hyperglycemia occurs as a side effect of prolonged use of certain drugs (glucocorticoids, estrogen, psychotropic drugs), when exposed to toxic substances.
Hyperglycemia signals diabetes only in the presence of insulin errors, the appearance of symptoms of sugar disease.
Types of diabetic pathology

Diabetes mellitus is a violation of carbohydrate and water metabolism in the body.
Classification of WHO determines two leading types of disease: insulin -dependent (I type) and the opposite form - insulin -dependent diabetes (II type). They differ in reasons for the appearance and details of pathogenesis, the nature of the course, have their own characteristics of treatment, but the consequences are as dangerous.
- Insulin -dependent (juvenile) diabetes is caused by the autoimmune aggression of the body. The affected endocrine beta cells are not able to produce insulin in the necessary doses, its constant administration from the outside is required. Persons under 30 years old, thin. The disease begins suddenly, quickly progresses and has a severe course.
- Insulinone -dependent. The causes of the disease of diabetes of this type are heredity and obesity. Insulin can be produced in sufficient quantities, but the cells are not sensitive to it. This is due to an excess of nutrients. Diabetics over 40, have a complete physique. The acquired diabetes develops gradually, proceeds stably. Most patients suffer from this type of disease.
Severity
The severity of the development of diabetes mellitus at the stage of glycemia, glucosuria, the degree of dysfunction of the target organs, the presence of complications are determined, which shows the compensation capabilities of the body. There are 4 degrees of severity. If diabetes passes to a mild degree, then treatment and nutrition are selected correctly. The degree of diabetes and symptoms are described in the table.
| Degree | Blood sugar, mmol/l | Urine readings | Symptoms |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1st (light) | No more than 7 | Protein is normal, glucosuria is absent | Absent |
| 2nd (middle) | 7-10 | Glucose up to 40 g/l; Ketosis and ketoacidosis periodically appear | Malfunctions of the cardiac activity, visual apparatus, nervous system, manifestation of angioneropathy |
| 3rd (heavy) | 10-14 | Persistent glucosuria 40 g/l, a lot of protein, ketone bodies | Enhanced effect on organs, a drop in vision, pain and numbness in the legs, increase in blood pressure |
| 4th (superpolate) | 15-25 | More than 50 g/l glucose, intense proteinuria and ketoacidosis | Strong defeat of all organs, renal failure, diabetic coma, gangrene, ulcerative foci on the legs |
Characteristic symptoms of diabetes
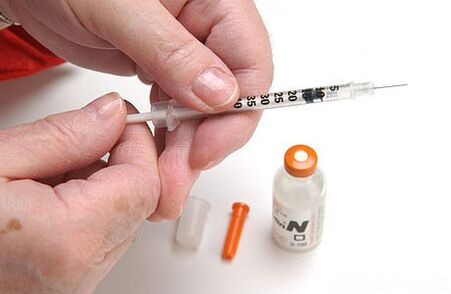
The clinical signs of the disease in most cases are characterized by a gradual course.
Diabetes in adults may not immediately declare themselves that it leads to the development of complications. Type I diabetes are developing rapidly with high glycemia and coma. The intensity of the symptoms of acquired diabetes is associated with the degree of insulin products deficiency, the individuality of the patient's body. You need to go through a test to determine the degree of sugary of the blood, if one of the symptoms appears:
- an unusual sensation of dry mouth;
- the inability to quench thirst;
- enhanced diuresis - an increase in the amount of urine displayed;
- quick weight loss or weight gain;
- itchy and dry skin;
- reduced skin sensitivity on the feet;
- numbness, tingling in legs and arms;
- convulsions, severity in the legs;
- purulent skin processes caused by slow skin regeneration;
- low resistance to infections;
- constant feeling of hunger;
- vague vision;
- increased blood pressure;
- swelling of the face and legs;
- Pain in the head, fainting;
- Acetone smell of the body;
- darkenness of consciousness;
- pseudo -peritritin (false "sharp stomach").
The consequences of glycemia
Diabetes mellitus is an insidious disease. Excess blood sugar harms blood vessels, causes wall damage. Excess glucose is transformed into fat deposits. This leads to obesity and steatogepatosis (accumulation of lipids in hepatic cells). Glucose causes glycolization of membrane proteins. The oxidative process is able to cause impaired protein functioning and the appearance of toxic by -products. Defective proteins cause disturbances in the structure of organs. The accumulation of toxins and ketones causes damage to the nervous system of the patient, up to disorders in the mind and coma. Excessive blood cholesterol settles on the arterial walls in damaged areas and forms plaques of atherosclerosis, contributing to the angiopathies of the eyes, vessels of the legs and other organs.
The degree of excess of the level of blood glucose determines the complexity of the course of the disease.
The risk of complications
Complicated diabetes mellitus carries the danger of the life of a sick person, so it is so important to identify the ailment in time and begin treatment. The disease is aggravated for 10-15 years. The complications that appear progress quickly and it is not easy to cope with them. Acute complications with primary diabetes (hypo- and hyperglycemia) are caused by sharp fluctuations in blood sugar. A list of states that complicate the disease of diabetics:
- Hypoglycemia - a sharp drop in glucose less than 3 mmol/l can lead to a hypoglycemic coma.
- Hyperglycemia - lifting the sugar indicator above 6 mmol/l ends with a hyperglycemic coma.
- Ketoacidosis - damage to neurons with ketone bodies, causing someone.
- Neuropathy - damage to the nerves of the periphery.
- Diabetic foot, trophic ulcers and deadlines of the lower extremities caused by angiopathy and neuropathy.
- Nephropathy - damage to the small capillaries of the kidneys, which disrupts the functioning of the urinary system.
- Retinopathy - thinning of the vascular walls of the retina.
- Cardiomyopathy - disorders in the heart muscle.
- Encephalopathy - pathology in cerebral vessels.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of diabetes determines the type of disease, severity, the presence of lesions of internal organs. Studies can be conducted repeatedly to assess the degree of progress of the disease and the effect of treatment. Diagnostic criteria for diabetes are characteristic signs of diabetes and the degree of lifting of glucose. To confirm the diagnosis, urine and blood tests, instrumental studies are done:
- indications of glucose on an empty stomach;
- glycemic profile (daily vibrations);
- blood on an insulin level;
- a study of glucose tolerance, the ratio of sugar on an empty stomach and after the consumption of carbohydrates;
- analysis for glycolized hemoglobin;
- blood for biochemistry;
- general urine analysis detecting glucose, proteins;
- electrolyte blood test;
- acetone indicators in the urine;
- eye view inspection;
- Rebell test for kidney damage;
- Ultrasound of the abdomen;
- cardiogram for checking the function of the heart;
- Capillaryoscopy, reuroscopy of the lower extremities determines the degree of defects in the vessels.
In healthy people, the level of glucose in the blood is in the range of 3. 3-5. 5 mmol/l.
Treatment of the disease

In the presence of suspicion of diabetes mellitus, this diagnosis must be either confirmed or refuted.
Diabetes mellitus is a chronic pathology that needs to be treated for life.
The principles of treatment of diabetes - sugar control in the bloodstream glucometer and the prevention of complications by observing the diet and taking drugs.
An endocrinologist can treat the disease, a cardiologist, a neuropathologist, an ophthalmologist, a vascular surgeon are connected.
Modern methods of treatment - medicines, diet, physical education - slow down the progression of the disease.
Medicines
The doctor selects the medicine, given the type of the disease. Type 1 diabetes mellitus requires only insulin therapy, type 2 diabetes can be treated with sugar. The tablets act on the pancreas, increase the sensitivity of peripheral tissues. Such drugs are used:
- Sulfanilamides.
- Biguanides.
- Insulin preparations of short and prolonged action. Simple insulin is administered 3-5 times a day, and long -acting insulin up to 2 doses. Perhaps combined use of drugs.
Diet with diabetes
Treatment of diabetes certainly includes a diet with the selection of calorie content, excluding easily digestible carbohydrates, sweets. Diabetes requires fractional power. At the same time, the ratio of nutrients remains close to physiological. Sugar is replaced by xylitol or sorbitol. In the middle and severe forms of the disease, diet No. 9 is recommended. It is allowed to eat vegetable soups, low-fat types of fish and meat, sour milk products and cheese, cereals (buckwheat, barley oatmeal), fruits, berries of sweet and sour taste. You can never eat sdoba, sweets, fatty dishes, rice semolina, pasta, grapes, salty, marinated vegetables.
Prevention
The occurrence of type 1 disease can not always be influenced, since it can provoke a viral pathogen. The reason for the development of type 2 diabetes is considered an unhealthy lifestyle, especially in people with hereditary prerequisites. Prevention measures if sugar disease is diagnosed: proper nutrition in small portions with a minimum of easily digestible carbohydrates and fat, maintaining optimal body weight. Hypertension is also carried out with the control of blood pressure numbers. Periodically, you need to donate blood for the content of glucose and lipid blood fractions. Moderate physical activity will help to keep the body in tone.